Indirect Taxes and Subsidies
- SupplyYourDemand

- Jun 27, 2020
- 1 min read
INDIRECT TAXES
Taxes on consumption
The more inelastic demand is, the more of an indirect tax is passed onto consumers.

Impact of Indirect Taxes on Government:
Indirect taxes generate government revenue.
These revenues can be spent on capital investment or transfer payments.
Indirect taxes are used to correct market failures (eg. externalities)
EVAL: If demand is perfectly inelastic, the burden of tax would fall completely on consumers.
Impact of Indirect Taxes on Consumers and Producers:
If demand is perfectly inelastic, the burden of the tax will fall completely on the consumer.
If demand is perfectly elastic, the burden of the tax will fall completely on the producer.
SUBSIDIES:
Can correct market failure by encouraging the consumption and production of a good with positive externalities.
A subsidy will shift the supply curve rightwards.
Quantity produced will increase and price will fall.
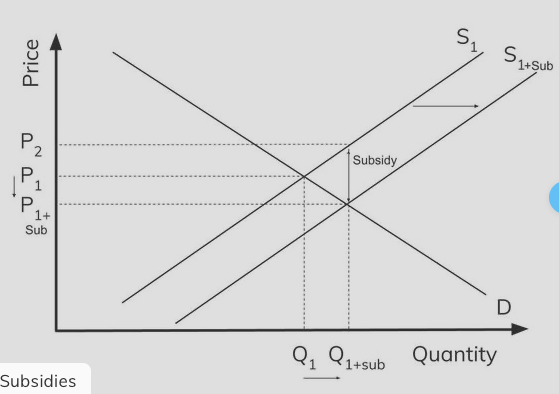
Consumers: consumer surplus rises as the price that consumers pay has fallen and output has risen.
Producers: Producer surplus rises because the price consumers pay + subsidy is higher than the price at the previous market equilibrium
Governments: Must pay for subsidies using tax revenues or borrowing
EVAL: Opportunity costs
Authored by Priscilla Chau.



Comments